Satellite
In the context of spaceflight, a satellite is an object which has been placed into orbit by human endeavor. Such objects are sometimes called artificial satellites to distinguish them from natural satellites such as the Moon
In satellite communication, signal transferring between the sender and receiver is done with the help of satellite. In this process, the signal which is basically a beam of modulated microwaves is sent towards the satellite. Then the satellite amplifies the signal and sent it back to the receiver’s antenna present on the earth’s surface. So, all the signal transferring is happening in space. Thus this type of communication is known as space communication
Multiple Access Defined
Multiple access in satellite terms involves running communication streams between multiple satellite conduits or terminals at the same time. Normally, in simple traffic a terminal only handles one stream at a time. This approach doesn’t work when a satellite’s owner needs it to function managing thousands of points simultaneously. As a result, satellite technology today works with three different systems that offer multiple access ability.
Types of Multiple Access Methods
There are three types of Multiple Access Methods:
- Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) – flexible and simple
- Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) – popular
- Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA Spread Spectrum) – highly secure
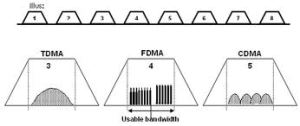
Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA)
- Satellite frequency is already broken into bands, and is broken in to smaller channels in Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA)
- Overall bandwidth within a frequency band is increased due to frequency reuse (a frequency is used by two carriers with orthogonal polarization)
- The number of sub-channels is limited by three factors:
- FDMA can be performed in two ways:
- Fixed-assignment multiple access (FAMA): The sub-channel assignments are of a fixed allotment. Ideal for broadcast satellite communication
- Demand-assignment multiple access (DAMA): The sub-channel allotment changes based on demand. Ideal for point to point communication
Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA)
- TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access) breaks a transmission into multiple time slots, each one dedicated to a different transmitter
- TDMA is increasingly becoming more widespread in satellite communication
- TDMA uses the same techniques (FAMA and DAMA) as FDMA does

Advantages of TDMA over FDMA.
- Digital equipment used in time division multiplexing is increasingly becoming cheaper
- There are advantages in digital transmission techniques. Ex: error correction
- Lack of inter-modulation noise means increased efficiency
Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA Spread Spectrum)
- CDMA, also called spread spectrum communication, differs from FDMA and TDMA because it allows users to literally transmit on top of each other
- This feature has allowed CDMA to gain attention in commercial satellite communication
- It was originally developed for use in military satellite communication where its inherent anti-jam and security features are highly desirable
- CDMA was adopted in cellular mobile telephone as an interference-tolerant communication technology that increases capacity above analog systems
- Two forms of CDMA are applied in practice:
- Direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS)
- Frequency hopping spread spectrum (FHSS)
FHSS has been used by the OmniTracs and Eutel-Tracs mobile messaging systems for more than 10 years now, and only recently has it been applied in the consumer’s commercial world in the form of the Bluetooth wireless LAN standard. However, most CDMA applications over commercial satellites employ DSSS (as do the cellular networks developed by Qualcomm)
- A typical CDMA receiver must carry out the following functions in order to acquire the signal, maintain synchronization, and reliably recover the data:
Summary
- The bottom line in multiple access is that there is no single system that provides a universal answer
- FDMA, TDMA, and CDMA will each continue to have a place in building the applications of the future
- They can all be applied to digital communications and satellite links
- When a specific application is considered, it is recommended to perform the comparison to make the most intelligent selection
References
http://www.en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Channel_access_method
http://www.ehow.com/about_6814542_multiple-access-techniques-satellite-communication.html
courses.missouristate.edu/huiliu/csc690/slides/satellite.ppt